Sudoku Course:

Welcome to Course in Sudoku
Part 1
Introduction
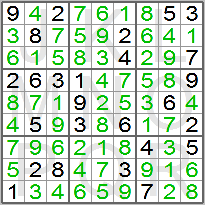 The popular game Sudoku is based on placing the digits 1 to 9 on a square board with
81 squares. The board has 9 rows, 9 columns and 9 boxes of 3 x 3 squares. Within
each group of squares – row, column and box -
The popular game Sudoku is based on placing the digits 1 to 9 on a square board with
81 squares. The board has 9 rows, 9 columns and 9 boxes of 3 x 3 squares. Within
each group of squares – row, column and box -
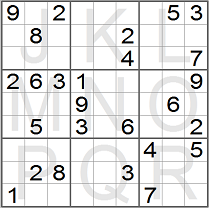 At the beginning of the game some of the squares hold a digit (the given digits or
clues). Your job is to fill the empty squares with digits, which have not yet been
used, so that each row, column and box in the end will hold all the digits from 1
to 9. Thus each square contributes to or is a part of three groups: a row, a column
and a box. In each of the groups the digits from 1 to 9 should be placed.
At the beginning of the game some of the squares hold a digit (the given digits or
clues). Your job is to fill the empty squares with digits, which have not yet been
used, so that each row, column and box in the end will hold all the digits from 1
to 9. Thus each square contributes to or is a part of three groups: a row, a column
and a box. In each of the groups the digits from 1 to 9 should be placed.
Use Logic
A Sudoku puzzle is solved by logic -
Sudoku puzzles can be made with any degree of difficulty, so there would be challenging puzzles for anyone to solve, from the beginner to the extremely skilled.
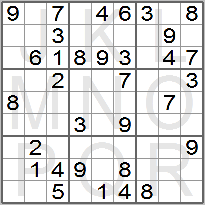 The easy puzzles generally have a larger number of given digits or clues (30 or more).
The easy puzzles generally have a larger number of given digits or clues (30 or more).
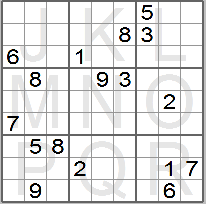 The most difficult, which can be extremely difficult to solve, would generally have
a lesser number of clues (down to 17).
The most difficult, which can be extremely difficult to solve, would generally have
a lesser number of clues (down to 17).
Solving Sudoku
The best way of starting solving is to locate the most crowded part of the sudoku board where you get the most help.
Method 1
Try to look at a row of boxes or a column of boxes. Try to locate two of the same digit.
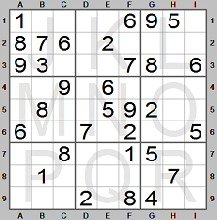 Look at the upper row of boxes (rows 1, 2 and 3). Go through the digits: there are
two of 7, two of 8 and two of 9. Looking first at 7, this digit is missing in row
1. The only square it can be is I1.
Look at the upper row of boxes (rows 1, 2 and 3). Go through the digits: there are
two of 7, two of 8 and two of 9. Looking first at 7, this digit is missing in row
1. The only square it can be is I1.
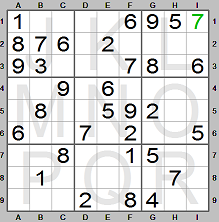 We place 7 in square I1. Now look at digit 8. It is missing in row 1. It can be in
square D1 and E1, but we cannot at the moment determine in which square (D1 or E1)
it should be. Look then at digit 9. It is missing in row 2. It can only be in square
D2 since there is already a 9 in column F.
We place 7 in square I1. Now look at digit 8. It is missing in row 1. It can be in
square D1 and E1, but we cannot at the moment determine in which square (D1 or E1)
it should be. Look then at digit 9. It is missing in row 2. It can only be in square
D2 since there is already a 9 in column F.
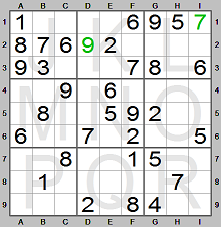 We place 9 in square D2. Now look at the right column of boxes (columns G, H and
I). There are two of 7. This digit is missing in column G. Digit 7 can only be in
square G4 since there is a 7 in row 6.
We place 9 in square D2. Now look at the right column of boxes (columns G, H and
I). There are two of 7. This digit is missing in column G. Digit 7 can only be in
square G4 since there is a 7 in row 6.
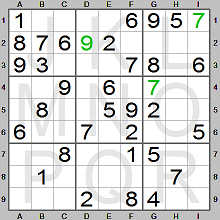 We place 7 in square G4. Now look at the middle row of boxes (rows 4, 5 and 6). There
are two of 6. It is missing in row 5. It can only be in square H5 since there is
a 6 in column I.
We place 7 in square G4. Now look at the middle row of boxes (rows 4, 5 and 6). There
are two of 6. It is missing in row 5. It can only be in square H5 since there is
a 6 in column I.
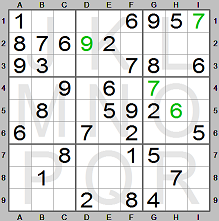 We place 6 in square H5. Still looking at the middle row of boxes (rows 4, 5 and
6) there are two of 9. It is missing in row 6. It can only be in square H6 since
there is a 9 in column G.
We place 6 in square H5. Still looking at the middle row of boxes (rows 4, 5 and
6) there are two of 9. It is missing in row 6. It can only be in square H6 since
there is a 9 in column G.
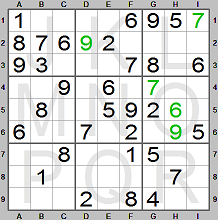 We place 9 in square H6.
We place 9 in square H6.
You can continue with this technique and solve the puzzle further.
However, another method can also be useful in later stages of the solving process.
Method 2
Using this method you focus on a row, column or box with 5 or more digits.
The upper left box has 6 digits. A 5 is missing. Since there is a 5 in row 1 it can only be in square C3. You can place 5 in that square.
In the upper right box having 5 digits 2 is missing. Since there is a 2 in row 2 it can only be in square H3. You can place 2 in that square.
In column G having 6 digits 6 is missing. Since there is a 6 in the upper two right boxes, digit 6 can only be in square G8. You can place 6 in that square.
Using the simple methods 1 and 2 most easy sudoku puzzles can be solved completely.
The Candidate Table
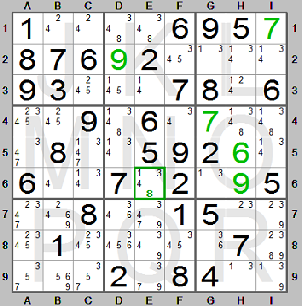 A great help in solving sudoku is to make a table (the candidate table) of possible
candidate digits, which may be placed in each of the empty squares at each stage.
A great help in solving sudoku is to make a table (the candidate table) of possible
candidate digits, which may be placed in each of the empty squares at each stage.
The Sudoku Instructions program can automatically calculate the candidate table and show it directly on the sudoku board in such way that you can see the possible digits (the candidate digits) for each of the empty squares.
A single candidate may be hidden among other candidates in a square (hidden single candidate). In the shown sudoku board digit 8 is a hidden single candidate in square E6 since in row 6 digit 8 can only be in that square. The Sudoku Instructions program shows the single candidate digit in green bold type in the square marked with a green frame.
If a square has only one candidate (an isolated single candidate), then that digit should be placed in the square. In the sudoku board above digit 4 is an isolated single candidate in square B6. All the other digits are present either within the box, row or column of which B6 is a part. Digit 4 is the only digit left for that square.
If the candidate table is displayed it will be very easy to locate the isolated single candidates.
If the candidate table is not displayed it will be easier to locate hidden single candidates. They correspond to the digits found using method 1 described above.
The Sudoku Instructions Program can help you find single candidates. It will first try to find hidden single candidates. Then it will look for isolated single candidates.
When you find a square with a single candidate, you can place that digit in the square. Then that candidate digit needs to be removed from the candidate table for the three groups (row, column and box) of which the square is a part. The Sudoku Instructions Program does this automatically.
The methods described here are the most important ones. Using them most easy Sudoku puzzles can be solved.
However, to solve more difficult puzzles at some stage it may no longer be possible to find single candidates.
Thus it may be necessary to reduce the number of candidates for single candidates to emerge. Only then will it be possible to solve the puzzle without trial and error.
In the following parts of the course we will describe various methods for candidate reduction.
Happy Sudoku Solving!
© Sudoku Instructions Programming Unit -